The Director-General of the World Health Organization (WHO), following the third meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) (IHR) Emergency Committee regarding the upsurge of mpox 2024, held on 25 February 2025, from 12:00 to 17:00 CET, concurs with its advice that the event continues to meet the criteria of a public health emergency of international concern and, considering the advice of the Committee, he is hereby issuing a revised set of temporary recommendations.
The WHO Director-General expresses his most sincere gratitude to the Chair, Members, and Advisors of the Committee. The proceeding of the third meeting of the Committee will be shared with States Parties to the IHR and published in the coming days.
Temporary recommendations
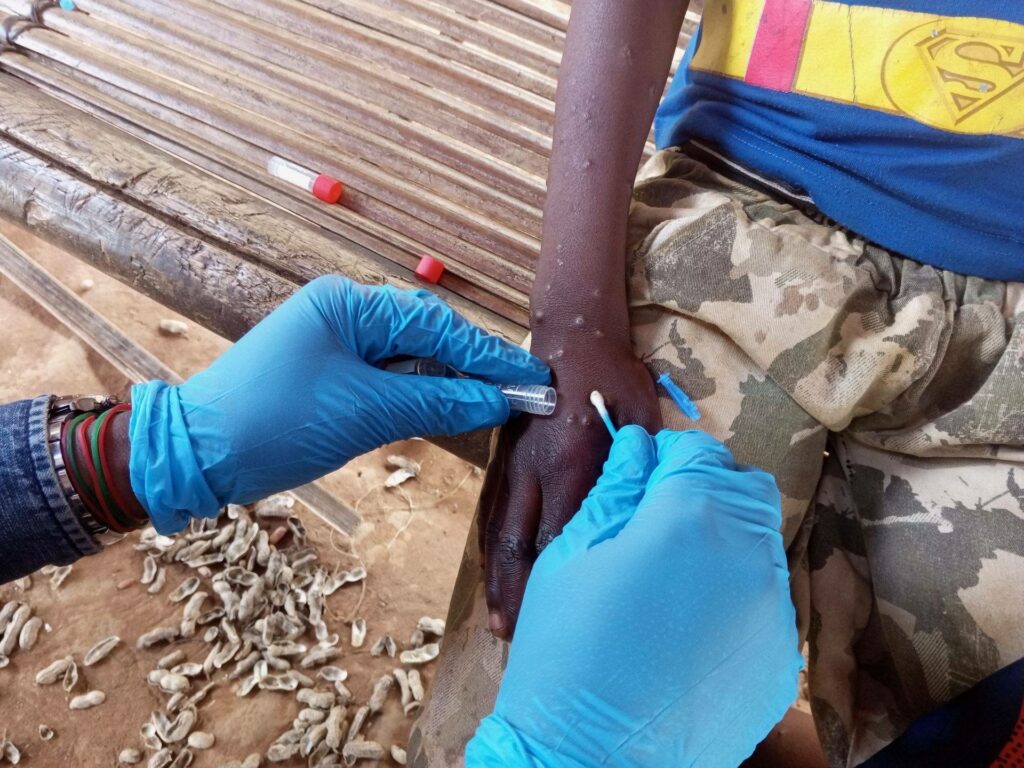
These temporary recommendations are issued to States Parties experiencing the transmission of monkeypox virus (MPXV), including, but not limited to, those where there is sustained community transmission, and where there are clusters of cases or sporadic travel-related cases of MPXV clade Ib.
They are intended to be implemented by those States Parties in addition to the current standing recommendations for mpox, which will be extended until 20 August 2025.
In the context of the global efforts to prevent and control the spread of mpox disease outlined in the WHO Strategic framework for enhancing prevention and control of mpox- 2024-2027, the aforementioned standing recommendations apply to all States Parties.
All current WHO interim technical guidance can be accessed on this page of the WHO website. WHO evidence-based guidance has been and will continue to be updated in line with the evolving situation, updated scientific evidence, and WHO risk assessment to support States Parties in the implementation of the WHO Strategic Framework for enhancing mpox prevention and control.
Pursuant to Article 3 Principle of the International Health Regulations (2005) (IHR), the implementation of these temporary recommendations, as well as of the standing recommendations for mpox, by States Parties shall be with full respect for the dignity, human rights and fundamental freedoms of persons, in line with the principles set out in Article 3 of the IHR.
Emergency coordination
Secure political commitment, engagement and adequate resource allocation to intensify mpox prevention and response efforts for the lowest administrative and operational level reporting mpox cases in the prior 4 weeks.
Establish or enhance national and local emergency prevention and response coordination arrangements as recommended in the WHO Mpox global strategic preparedness and response plan (2024), and its upcoming iteration, and in line with the WHO Strategic framework for enhancing prevention and control of mpox (2024-2027) to maintain.
Establish or enhance coordination among all partners and stakeholders engaged in or supporting mpox prevention and response activities through cooperation, including by introducing accountability mechanisms.
Establish a mechanism to monitor the effectiveness of mpox prevention and response measures implemented at lower administrative levels, so that such measures can be adjusted as needed.
Strengthen coordination and response mechanisms, particularly in humanitarian and conflict-affected areas, by engaging local and national authorities and implementing partners to ensure integrated mpox surveillance and care delivery in support of vulnerable populations, especially in areas with population displacement and inadequate access to essential services.
Collaborative surveillance
Enhance mpox surveillance, by increasing the sensitivity of the approaches adopted and ensuring comprehensive geographic coverage.
Expand access to accurate, affordable and available diagnostics to test for mpox, including through strengthening arrangements for the transport of samples, the decentralization of testing and arrangements to differentiate MPXV clades and conduct genomic sequencing.
Read more on : https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2025-third-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-2005-emmergency-committee-regarding-the-upsurge-of-mpox-2024-temporary-recommendations
World Health Organization






OTHER ARTICLES
Editorial — Prevent, inform, and act for women’s health in Africa
Kenya : Government Prioritises Maternal Health and Strengthens Support for Community Health Promoters
Strengthening pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response capacities in Senegal using the “One Health” approach